Here is the list of 8 main air conditioning parts and description of their main operation in every air conditioning system.
1. air conditioning or heat pump compressor which compresses low pressure refrigerant gas into a high pressure, high temperature gas. Usually the compressor is in the outdoor portion of an air conditioning or heat pump system. The air conditioner or heat pump compressor unit is basically a high pressure pump driven by an electric motor. The air conditioning compressor is usually packaged in the outdoor compressor or condenser unit.
2. A condenser or condensing unit: typically a condensing coil inside which high temperature high pressure refrigerant gas flows, and over which a fan blows air to cool the refrigerant gas back to a liquid state (thus transferring heat from the refrigerant gas to the air being blown by the fan). The condenser unit is basically a coil of finned tubing and a fan to blow air across the coil. Usually the condenser unit is in the outdoor portion of an air conditioning system, often packaged along with the compressor motor discussed above
3. A metering device which dispenses liquid refrigerant into an evaporator coil. The metering device may be simply a thin section of tubing (a capillary or “cap” tube) or it may be a bit more sophisticated thermostatic expansion valve (TEV) which includes a temperature sensing control that can open and shut the device against refrigerant flow.
4. An evaporator coil or cooling coil: typically the cooling coil is a section of finned tubing (it looks a lot like a car radiator) into which liquid refrigerant is metered and permitted to evaporate from liquid to gas state inside the coil. This state change of the refrigerant, from liquid to gas, absorbs heat, cooling the evaporator coil surface and thus cooling indoor air blown across the cooling coil. Usually the cooling coil is located inside the air handler.
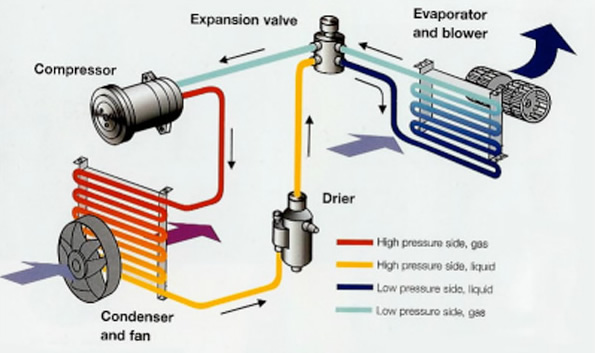 5. An air handler and blower unit which provides a fan to blow building air across or through the evaporator coil. The air handler blower fan unit moves building air across the evaporator coil surface in order to condition building air by cooling it (and thus also by removing moisture from the cooled air).
5. An air handler and blower unit which provides a fan to blow building air across or through the evaporator coil. The air handler blower fan unit moves building air across the evaporator coil surface in order to condition building air by cooling it (and thus also by removing moisture from the cooled air).
6. A duct system which distributes conditioned air from the air handler in to the occupied space (supply ducts), and which takes air from the occupied space and returns it to the cooling system air handler.
7. Heat Pump Systems use the same components we have described just above, with the addition of a reversing valve that in essence permits the system to run “backwards” in cold weather. So in air conditioning mode the heat pump is moving heat from inside the building to outdoors while in heating mode the heat pump is moving heat from outdoor air (or water in some designs) to the building interior.
8. Air conditioner controls and features, which include a room thermostat, electrical switches, fuses or circuit breakers, condensate handling system, and air filters
